Introduction to Pyramids
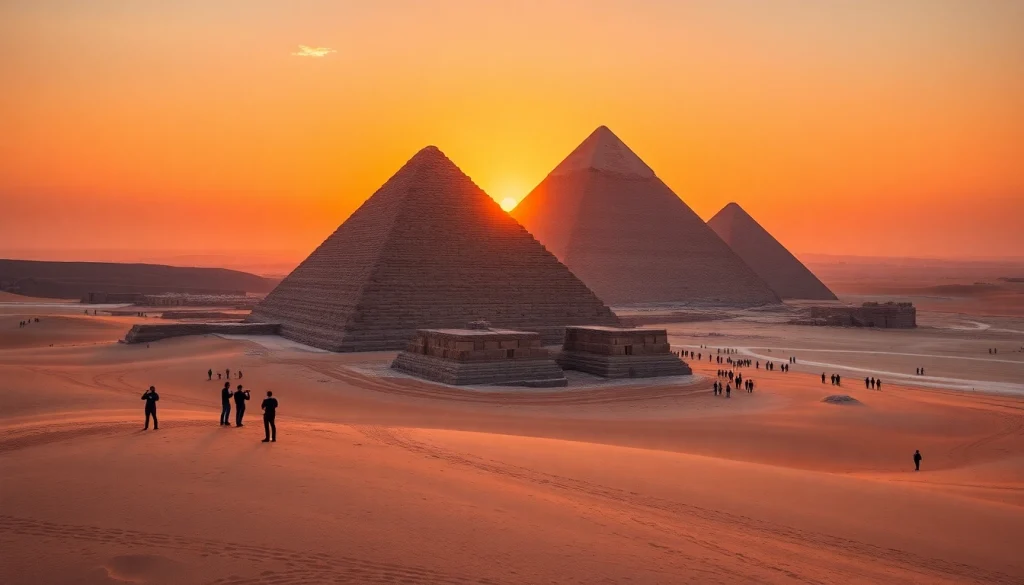
Pyramids are among the most fascinating architectural feats of ancient civilizations, symbolizing not only grandeur and power but also the mysteries of life and afterlife. Their monumental structures have intrigued scholars, archaeologists, and tourists alike, resulting in countless theories and legends surrounding their existence. A notable resource on the topic can be found at https://piraminds.com/. This article explores everything there is to know about pyramids, their significance in history, construction techniques, types, notable examples, and the mysteries that still surround them.
What Are Pyramids?
Pyramids are large, monumental structures that feature a polygonal base, rising to a single apex or vertex. They have been built by various cultures around the globe for different purposes. The most famous pyramids are the ones in Egypt, where they served primarily as royal tombs for pharaohs. The shape of the pyramid is often seen as symbolic, representing a stairway to the heavens or a bridge to the afterlife.
Historical Significance of Pyramids
The historical significance of pyramids cannot be overstated. In ancient Egypt, they served not only as burial sites but also as statements of power and divine connection. The pyramids of Giza, for example, are aligned with the stars and are believed to have been designed to facilitate the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife. Beyond Egypt, pyramids were constructed in regions like Mesoamerica, where they were often part of ceremonial complexes.
Different Types of Pyramids
Different cultures created various types of pyramids, each serving distinct purposes and possessing unique architectural styles. The most notable types include:
- Step Pyramids: These have a series of terraces or steps, with one of the earliest examples being the Pyramid of Djoser in Egypt.
- True Pyramids: Characterized by smooth sides, the Great Pyramid of Giza is the most recognized example.
- Mesoamerican Pyramids: Structures like the Pyramid of the Sun in Teotihuacan feature platforms and staircases, used for religious rites.
Construction Techniques of Pyramids
The construction of pyramids was a monumental task requiring advanced planning, innovative engineering, and a massive workforce. Understanding how these ancient builders worked gives us insight into their capabilities and the cultural significance of these structures.
Materials Used in Pyramid Construction
The materials used in pyramid construction varied depending on the location, available resources, and architectural goals. In Egypt, limestone and granite were the primary materials. The outer casing stones of the Giza pyramids were made of Tura limestone that reflected the sun’s light, making the structures visible from miles away.
Labor Force Involved in Building Pyramids
The workforce that built the pyramids consisted of skilled laborers, craftsmen, and artisans. Contrary to popular belief, they were not slaves but rather a paid workforce who often worked in rotating shifts. Estimates suggest that tens of thousands of workers were involved in the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, indicating a high degree of organization and logistics.
Innovative Engineering Methods
The engineering methods employed in pyramid construction were indeed innovative for their time. Techniques included the use of sledges to transport heavy stones and the application of ramps to move stones into position. Recent discoveries suggest that worker-led teams orchestrated these constructions, employing mathematical and astronomical knowledge to ensure precision in alignment and design.
Famous Pyramids Around the World
The legacy of pyramids stretches far beyond Egypt. Various countries and civilizations have built their unique pyramids, often reflecting their cultural beliefs and architectural skills.
The Giza Pyramids: A Closer Look
The Pyramids of Giza—specifically the Great Pyramid, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure—are considered among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Great Pyramid, originally standing at 146.6 meters, is the largest and is surrounded by complex mortuary temples and smaller pyramids designed for queens.
Other Notable Pyramids
Apart from those in Egypt, notable pyramids include:
- Pyramid of the Sun: Located in Teotihuacan, Mexico, this pyramid is one of the largest structures in Mesoamerica.
- Pyramid of Chichen Itza: Known as El Castillo, it served as a temple to the Mayan god Kukulkan.
- Nubian Pyramids: Found in modern-day Sudan, these pyramids were built by the Kingdom of Kush and resemble an inverted triangle.
Pyramids in Modern Culture
In contemporary culture, pyramids have inspired art, literature, films, and theoretical architecture. They symbolize mystery and power, often depicted in various forms of media including books like “The Da Vinci Code” and films showcasing Egyptian mythology. Moreover, pyramids have become tourist attractions, drawing millions annually who seek to witness their grandeur firsthand.
The Mysteries Surrounding Pyramids
Pyramids are enveloped in numerous mysteries, fueling theories and speculations for centuries. The precise methods of construction, the exact reasons they were built, and what lies within them are topics of debate.
What Secrets Do Pyramids Hold?
Many scholars believe that pyramids may contain hidden chambers and artifacts. Recent archaeological discoveries have confirmed the presence of undiscovered rooms within some Egyptian pyramids, suggesting that the original builders may have designed them to conceal sacred items or even extensive knowledge about the afterlife.
Theories About Pyramid Functionality
Various theories exist regarding the primary function of pyramids. While many agree that they served as tombs for pharaohs, some suggest they were also astronomical observatories, places of worship, or even sites for advanced technological experimentation in their era.
Ongoing Research and Discoveries
Ongoing research continues to uncover more about the pyramids. Projects using advanced imaging techniques, such as muon tomography, have identified new voids and structures, leading to renewed interest and investigation into pyramid construction techniques and their purposes.
FAQs About Pyramids
What was the purpose of the Egyptian pyramids?
The primary purpose of Egyptian pyramids was to serve as monumental tombs for pharaohs, helping their transition to the afterlife and showcasing their divine status.
How were the pyramids built without modern technology?
Pyramids were constructed using skilled labor, advanced engineering techniques, and simple tools. Workers utilized ramps, sledges, and brute force to move massive stones into place.
What are the main materials used for constructing pyramids?
Main materials for pyramids included limestone and granite. In Egypt, Tura limestone was often used for casing due to its reflective quality, while granite was used for structural elements.
Are there pyramids outside of Egypt?
Yes, there are pyramids in several regions including Mesoamerica (e.g., Chichen Itza) and Nubia (Sudan). These structures often served different cultural and religious purposes.
What role do pyramids play in ancient Egyptian mythology?
Pyramids were deeply embedded in ancient Egyptian mythology, representing the pharaoh’s ascension to the afterlife and the belief in rebirth, connecting the earthly realm with the divine.